Ap Chem Reference Sheet
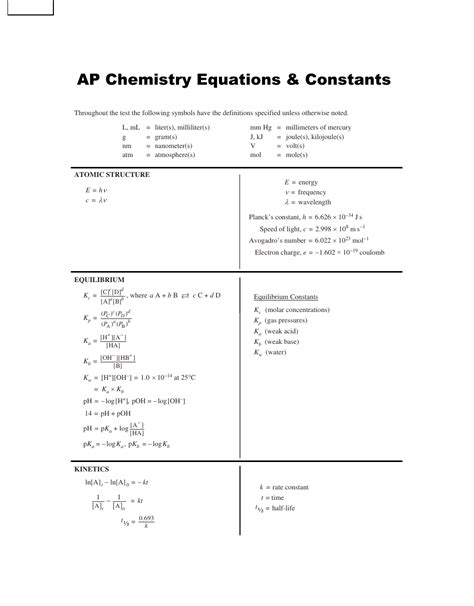
The Ultimate AP Chemistry Reference Sheet: Unlocking Exam Success

Embarking on the AP Chemistry journey can be both exciting and challenging. With a vast curriculum covering a range of chemical concepts, having a comprehensive reference sheet is invaluable. This guide aims to provide you with an expert overview, offering a concise yet detailed resource to enhance your understanding and exam preparation.
Unraveling the AP Chemistry Syllabus

The AP Chemistry course delves into the fundamental principles of chemistry, exploring topics that span the periodic table, chemical reactions, and the behavior of matter. Here's an overview of the key areas you'll encounter:
- Atomic Structure and Periodicity: From protons to electrons, understanding the building blocks of atoms is crucial. This section covers the electron configurations, periodic trends, and how these properties influence chemical behavior.
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: Explore the intricate world of chemical bonds, including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Learn how these bonds dictate the properties and reactivity of substances.
- Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry: Dive into the heart of chemistry with an in-depth look at reaction types, balancing equations, and stoichiometric calculations. Master the art of predicting and quantifying chemical reactions.
- Gases and Kinetic Molecular Theory: Understand the behavior of gases, from ideal gas laws to real gas behavior. Delve into kinetic theory, exploring the motion and energy of particles.
- Solutions and Solubility: Explore the world of solutions, from concentration measurements to solubility rules. Learn how solutes and solvents interact to form homogeneous mixtures.
- Acids, Bases, and Equilibrium: This section uncovers the fascinating world of acid-base chemistry, including pH, buffer solutions, and the concept of chemical equilibrium.
- Chemical Kinetics and Equilibrium: Investigate reaction rates, factors influencing reaction speed, and the dynamic nature of equilibrium systems.
- Thermochemistry: Discover the relationship between chemical reactions and energy, exploring concepts like enthalpy, entropy, and free energy.
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry: Explore the transfer of electrons in redox reactions and the applications of electrochemistry in batteries and electrolysis.
- Nuclear Chemistry: A glimpse into the world of atomic nuclei, covering radioactive decay, nuclear reactions, and the applications of nuclear chemistry.
Mastering Key Concepts
AP Chemistry demands a deep understanding of core principles. Here's a closer look at some essential concepts:
Atomic Theory and Electron Configurations
The modern atomic theory forms the foundation of chemistry. Learn about the evolution of atomic models, from Dalton's atomic theory to the discovery of subatomic particles. Understand how electrons are arranged in energy levels and subshells, and how this configuration influences an atom's properties.
| Element | Atomic Number | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1s1 |
| Helium (He) | 2 | 1s2 |
| Carbon (C) | 6 | 1s2 2s2 2p2 |
| Oxygen (O) | 8 | 1s2 2s2 2p4 |

Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
Chemical bonds are the glue that holds molecules together. Understand the three primary types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic. Learn how to predict bond types based on electronegativity differences and how molecular geometry influences bond angles and molecule shapes.
- Ionic Bonding: Transfer of electrons, forming positive and negative ions.
- Covalent Bonding: Sharing of electrons, leading to stable electron pairs.
- Metallic Bonding: Unique bonding in metals, involving delocalized electrons.
Stoichiometry and Limiting Reactants
Stoichiometry is the art of calculating reactant and product quantities in chemical reactions. Master the process of balancing chemical equations and determining limiting reactants, which can influence the yield of a reaction.
Example Stoichiometry Problem:
Consider the reaction: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O. If you have 3 moles of hydrogen and 2 moles of oxygen, what's the limiting reactant, and how much water can be produced?
Solution: Oxygen is the limiting reactant, and you can produce 4 moles of water.
Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory
The behavior of gases is governed by a set of laws. Understand the ideal gas law and how it relates to pressure, volume, temperature, and the amount of gas. Delve into the kinetic theory, which explains gas behavior at the molecular level, including particle motion and energy distribution.
Combined Gas Law: p1V1 / T1 = p2V2 / T2
Practical Applications and Real-World Chemistry
AP Chemistry extends beyond theory, offering insights into the practical applications of chemical principles. Here's a glimpse into the real-world relevance of your studies:
Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry is vital in pharmaceutical research. Chemists use these principles to develop new drugs, ensuring precise quantities of reactants for optimal results.
Environmental Chemistry
Chemical equilibrium and acid-base reactions play a critical role in environmental science. From water quality monitoring to air pollution control, these concepts are essential for understanding and mitigating environmental issues.
Forensic Chemistry
Forensic scientists rely on chemical analysis to identify substances and determine their origin. From drug identification to arson investigations, chemical principles are key to solving crimes.
Study Strategies and Exam Preparation

As you prepare for the AP Chemistry exam, here are some strategies to enhance your learning and boost your confidence:
- Practice Regularly: Solve a variety of problems to reinforce your understanding. Practice makes perfect, especially in chemistry, where applying concepts is crucial.
- Review Key Equations: Master the equations covered in the course. Understanding when and how to apply them is essential for success.
- Study with Visual Aids: Utilize visual tools like molecular models, periodic table posters, and reaction diagrams to enhance your learning experience.
- Connect Concepts: Chemistry is interconnected. Look for relationships between topics to build a comprehensive understanding.
- Past Exam Questions: Review past AP Chemistry exams to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions asked.
FAQ
What is the role of the AP Chemistry exam in college admissions?
+
The AP Chemistry exam is highly regarded by colleges and universities. Achieving a strong score can demonstrate your academic abilities and may even earn you college credit, reducing the number of introductory courses you need to take.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills in AP Chemistry?
+
Practice is key! Work through a variety of problems, starting with simpler ones and gradually increasing the difficulty. Break down complex problems into manageable steps, and don’t hesitate to seek clarification on concepts you find challenging.
Are there online resources to supplement my AP Chemistry studies?
+
Absolutely! Many online platforms offer AP Chemistry review materials, practice questions, and video tutorials. Websites like Khan Academy and AP Classroom provide official resources, while YouTube has a wealth of chemistry-related channels offering informative videos.

